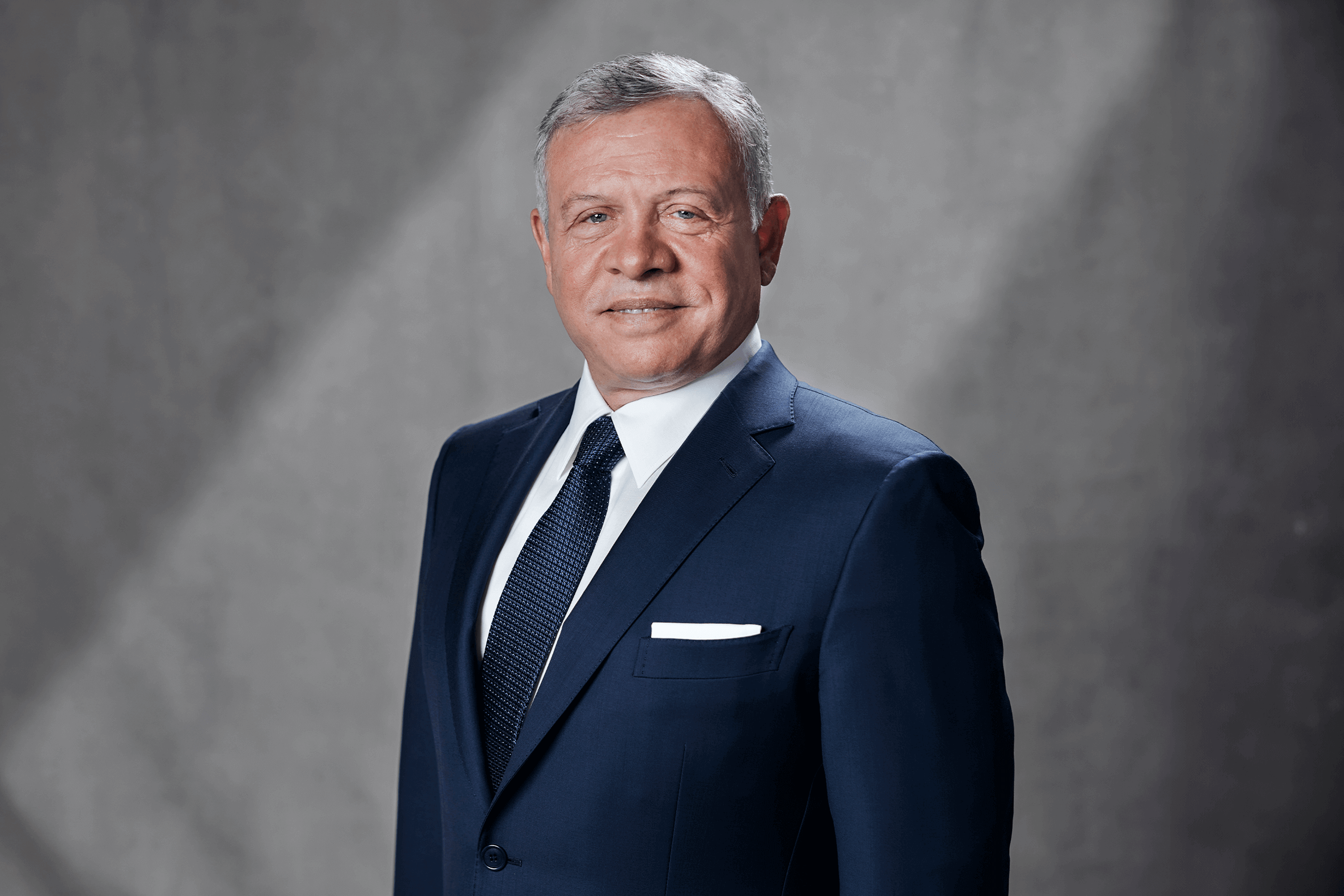
nightglow.info – King Abdullah II bin Al-Hussein, who has been Jordan’s monarch since 1999, is a pivotal figure in modern Middle Eastern politics. Known for his efforts to modernize Jordan, his pragmatic approach to regional diplomacy, and his focus on economic and social reforms, King Abdullah II has steered the country through challenging times while maintaining its stability. Under his leadership, Jordan has continued to be a key player in international peace efforts, particularly in the context of the Arab-Israeli conflict and regional stability.
Early Life and Education
Born on January 30, 1962, in Amman, Jordan, King Abdullah II is the eldest son of King Hussein and Queen Muna. His upbringing was steeped in the Hashemite tradition, with a strong emphasis on duty, leadership, and service to the nation. Abdullah received a prestigious education, attending St. Edmund’s School in Surrey, England, and later the Royal Military Academy Sandhurst, following in the footsteps of his father. He also attended Pembroke College at the University of Oxford, where he studied Middle Eastern affairs, and later Georgetown University in Washington, D.C., where he completed his studies in international affairs.
Before becoming king, Abdullah II pursued a career in the military, rising through the ranks of the Jordanian Armed Forces. His military experience earned him respect both domestically and internationally, providing him with a deep understanding of defense and security issues.
Ascension to the Throne
On February 7, 1999, King Hussein passed away after a long battle with cancer, and Abdullah II ascended to the throne. His succession came after a late decision by King Hussein to appoint Abdullah as his heir, replacing his brother Prince Hassan, who had long been designated as crown prince. Abdullah’s ascension was marked by a smooth transition, reflecting the stability of the Hashemite monarchy and the trust the Jordanian people had in their new leader.
From the outset, King Abdullah II faced significant challenges. Jordan’s economy was struggling, the peace process with Israel was at a standstill, and regional instability posed ongoing threats. Despite these obstacles, Abdullah II quickly demonstrated his commitment to modernizing Jordan and ensuring its continued stability in an unpredictable region.
Economic and Social Reforms
One of King Abdullah II’s primary focuses has been the modernization of Jordan’s economy. He has implemented a series of economic reforms aimed at liberalizing the economy, attracting foreign investment, and reducing poverty. Early in his reign, Abdullah II pushed for privatization of state-owned enterprises, deregulation of key industries, and the development of Jordan’s IT and service sectors. His vision was to turn Jordan into a regional hub for technology, business, and education.
Abdullah’s reforms have included strengthening Jordan’s infrastructure, expanding educational opportunities, and investing in renewable energy projects. The king has emphasized the need for innovation and entrepreneurship as engines of growth, promoting initiatives that encourage start-ups and small businesses. His efforts have helped diversify Jordan’s economy, though the country continues to face challenges due to its limited natural resources and reliance on foreign aid.
On the social front, King Abdullah II has been a strong advocate for women’s rights and youth empowerment. He has supported legislation to enhance gender equality, improve access to education, and create more opportunities for Jordan’s youth. In 2006, he launched the Madrasati Initiative, aimed at improving education in Jordan’s public schools, and he continues to emphasize the importance of modernizing the education system to prepare future generations for a competitive global economy.
Regional Diplomacy and Peace Efforts
King Abdullah II is widely respected for his diplomatic efforts to promote peace and stability in the Middle East. He has been a key mediator in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, advocating for a two-state solution and consistently calling for negotiations based on international resolutions. His advocacy for peace has earned him a reputation as a pragmatic leader committed to dialogue and cooperation.
Jordan’s strategic location, bordering Israel, the West Bank, Syria, Iraq, and Saudi Arabia, has placed the country at the heart of regional dynamics. Under King Abdullah II, Jordan has maintained strong relations with the United States, Europe, and other Western powers, while also engaging with Arab and Muslim countries. Jordan has been an essential ally in counterterrorism efforts, particularly in the fight against ISIS and other extremist groups in the region. King Abdullah II’s leadership in promoting interfaith dialogue, moderation, and tolerance has made Jordan a key partner in global efforts to combat extremism.
In 2015, King Abdullah II’s standing on the international stage was highlighted when Jordan was thrust into the spotlight following the brutal killing of a Jordanian pilot by ISIS. In response, Abdullah pledged a stronger fight against terrorism, and Jordan stepped up its military role in the coalition against ISIS. His commitment to protecting Jordan’s security and contributing to regional peace has been unwavering throughout his reign.
Domestic Challenges and Political Reforms
While King Abdullah II has implemented significant reforms, Jordan faces ongoing domestic challenges, particularly in the context of economic hardships and demands for greater political representation. The Arab Spring in 2011 saw widespread protests across the region, including in Jordan, where citizens called for political reforms, increased transparency, and better economic opportunities. In response, King Abdullah II initiated several political reforms, including changes to electoral laws, the establishment of constitutional courts, and the decentralization of power.
Although Jordan has avoided the large-scale unrest that other countries experienced during the Arab Spring, dissatisfaction with economic conditions and calls for more robust political participation have persisted. King Abdullah II has navigated these pressures by promoting gradual reform, maintaining stability, and preserving the monarchy’s central role in Jordanian governance.
International Leadership and Global Recognition
King Abdullah II is recognized globally for his leadership in promoting peace, security, and humanitarian efforts. He has played a critical role in addressing the Syrian refugee crisis, with Jordan hosting over a million Syrian refugees since the outbreak of the Syrian civil war in 2011. Despite the strain this has placed on Jordan’s resources, Abdullah has continued to advocate for international support for refugees and for political solutions to the region’s conflicts.
King Abdullah II has also championed interfaith dialogue and coexistence. His efforts to foster understanding between different religious communities have earned him international accolades. In 2010, he was awarded the Templeton Prize for his work in promoting religious harmony, and he continues to be an advocate for tolerance and moderation in a region often marked by sectarian tensions.
King Abdullah’s Vision for the Future
As King Abdullah II continues to lead Jordan, his focus remains on ensuring that the country remains stable, prosperous, and resilient in the face of regional challenges. His “Jordan 2025” vision outlines a comprehensive plan for economic development, political reform, and social progress, with an emphasis on sustainability, innovation, and inclusivity.
King Abdullah’s commitment to his people and his nation’s future is evident in his hands-on approach to governance. He frequently engages with citizens, listening to their concerns and working to address their needs. His leadership style, combining pragmatism, resilience, and a focus on reform, has earned him the respect of Jordanians and leaders worldwide.
Conclusion
King Abdullah II’s reign, which began in 1999, has been defined by his vision for a modern, stable, and peaceful Jordan. Through economic reforms, political modernization, and diplomatic efforts, he has positioned Jordan as a key player in the Middle East while maintaining the country’s internal stability in an often volatile region. King Abdullah’s leadership continues to shape Jordan’s future, ensuring that the Hashemite Kingdom remains a beacon of moderation and progress in the Arab world.